Foundations of Vulnerability Management: Strengthening Your Cybersecurity Posture
- 5 minutes read - 963 wordsIn today’s digital world, no organization is immune to cyber threats. From small businesses to global enterprises, everyone is a potential target for hackers seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. Whether you’re a seasoned cybersecurity professional or a curious beginner, understanding vulnerability management is key to safeguarding your systems and data.
In this post, we’ll break down the basics of vulnerability management, explain why it’s important, and provide steps for implementing an effective vulnerability management program.
What is Vulnerability Management?
At its core, vulnerability management is the process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and remediating security weaknesses in your organization’s systems, networks, and applications. These weaknesses, or vulnerabilities, can be exploited by attackers to compromise your data or gain unauthorized access.
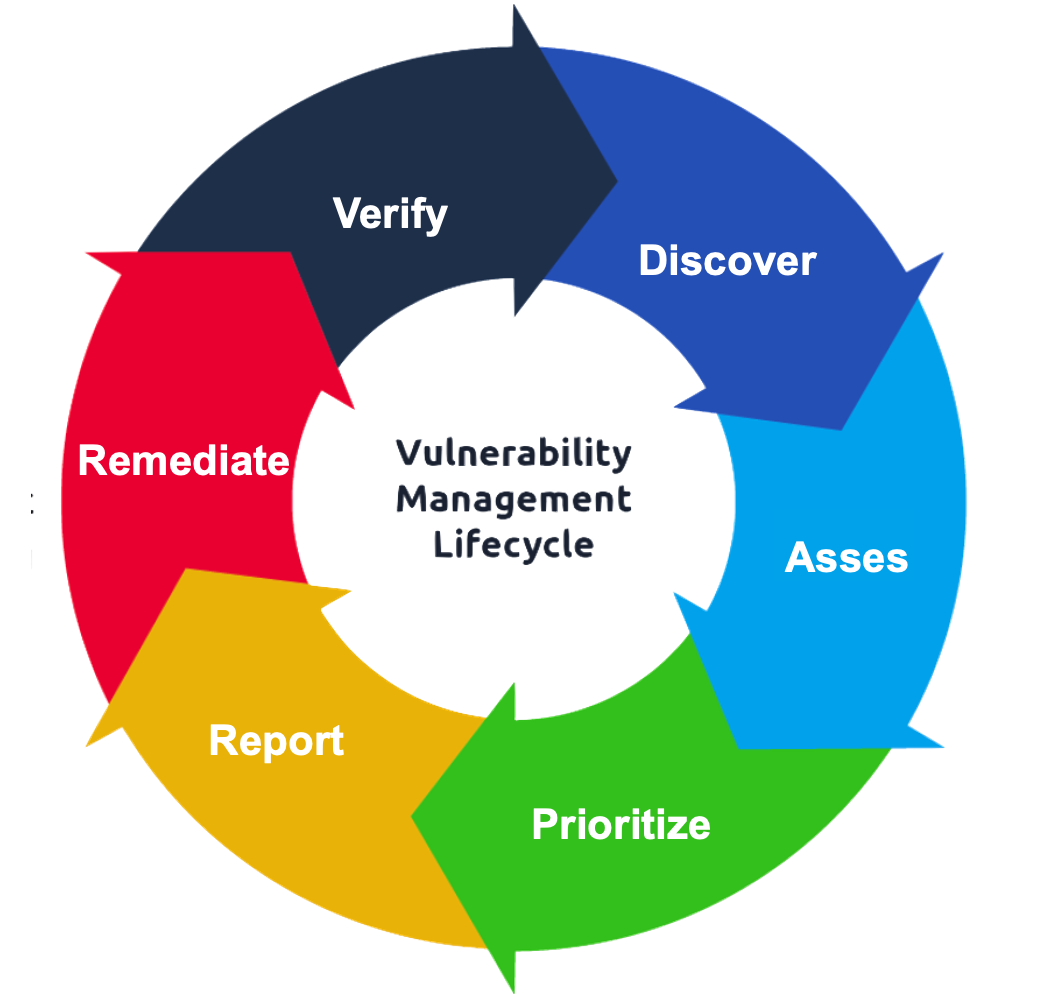
Image Source: Yotam Perkal, Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
A good analogy is to think of vulnerabilities like holes in a ship’s hull. If not patched, water (in this case, malicious attackers) can seep in, potentially sinking the entire ship.
Why is Vulnerability Management Important?
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities are discovered every day. A single unpatched flaw could lead to a major security breach, exposing sensitive information or causing downtime. Effective vulnerability management helps you:
- Minimize security risks by staying ahead of potential threats.
- Maintain compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, or PCI-DSS.
- Enhance operational efficiency by reducing the number of security incidents and the costs associated with them.
Without a robust vulnerability management process, organizations are left exposed, and hackers are more than happy to exploit these opportunities.
The Vulnerability Management Process
An effective vulnerability management program follows a structured, cyclical process that ensures ongoing protection. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
1. Identification
The first step is to identify vulnerabilities within your environment. This can be done through vulnerability scans using specialized tools like Nessus, Qualys, or Rapid7. These tools scan your network, devices, and applications to detect known vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
Regular scans are crucial to stay updated on potential risks. Remember, new vulnerabilities emerge frequently, so this step needs to be continuous, not a one-time event.
2. Assessment
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is to assess their severity. Not all vulnerabilities carry the same risk. Some may have little to no impact, while others could be critical and need immediate attention.
A common method for assessing vulnerability risk is the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System), which rates vulnerabilities on a scale of 0-10. The higher the score, the more severe the vulnerability. This step helps you prioritize which issues need to be addressed first.
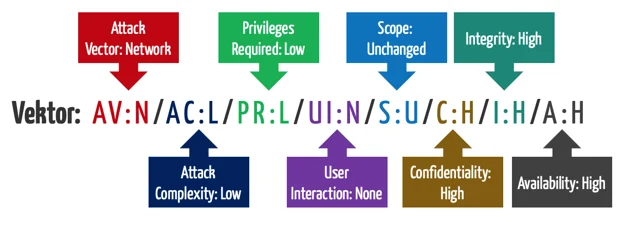
Image Source: Picus Security, What is Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
3. Prioritization
With the assessment in hand, the next challenge is deciding which vulnerabilities to tackle first. Typically, organizations prioritize based on:
- Severity score (e.g., critical vulnerabilities get fixed first).
- Exposure level (e.g., vulnerabilities in publicly accessible systems are prioritized).
- Impact on business operations (e.g., vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure).
4. Remediation
After prioritization, it’s time to act. Remediation involves taking steps to fix or mitigate the vulnerabilities. Common methods include:
- Patching: Applying updates or security patches provided by software vendors.
- Workarounds: Implementing temporary fixes or changes to mitigate risk if a patch is unavailable.
- System configuration: Adjusting system settings to reduce exposure.
In some cases, certain vulnerabilities may not be fully remediable. In these instances, organizations may choose to accept the risk or develop a plan to mitigate the potential impact.
5. Reporting & Continuous Monitoring
Vulnerability management is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. Once vulnerabilities are addressed, reporting plays a critical role in documenting what’s been fixed and what remains to be done. Continuous monitoring ensures that new vulnerabilities are detected promptly and that remediated vulnerabilities don’t resurface.
Tools like dashboards or reports help organizations keep track of their vulnerability management efforts, maintain compliance, and demonstrate the efficacy of their cybersecurity program.
Tools for Vulnerability Management
Here are some popular tools used by organizations to automate and streamline their vulnerability management processes:
- Nessus: Widely used for vulnerability scanning and compliance checks.
- Qualys: Offers cloud-based vulnerability management along with asset discovery and reporting features.
- Rapid7: Provides end-to-end vulnerability management, integrating threat intelligence to prioritize risks.
- OpenVAS: An open-source option that provides comprehensive vulnerability scanning.
Image Source: BSI, OpenVAS
Best Practices for Effective Vulnerability Management
To ensure the success of your vulnerability management efforts, consider the following best practices:
- Automate where possible: Leverage automated scanning tools and patch management solutions to streamline processes and reduce human error.
- Schedule regular scans: Set up a routine for scanning systems and applications. Quarterly or monthly scans are typical, but some high-risk environments may require more frequent scans.
- Patch promptly: Develop a patch management strategy to ensure that high-priority vulnerabilities are addressed as quickly as possible.
- Collaborate across teams: Work closely with IT, DevOps, and other teams to ensure vulnerabilities are understood and fixed without disrupting operations.
- Stay informed: Keep up with the latest vulnerabilities and security news. Subscribing to threat intelligence feeds or vulnerability databases (such as NVD) helps you stay ahead.
Closing Out
Vulnerability management is a critical component of any cybersecurity strategy. By following the steps outlined in this guide—identification, assessment, prioritization, remediation, and continuous monitoring—your organization can significantly reduce the risk of a cyber attack and protect its assets.
Whether you’re just starting out or you’ve been working in cybersecurity for years, a solid vulnerability management program is key to staying secure in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Start small, stay consistent, and remember that cybersecurity is a continuous journey.
Thanks for reading,
Michael
If you enjoy the content, then consider buying me a coffee.
P.S. Ready to enhance your vulnerability management process? Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity trends and best practices by subscribing to our newsletter or leaving your thoughts in the comments below! Visit CyberSHIELD