Building Blocks of a Security Program: Aligning with NIST Framework & SOC 2 Controls
- 6 minutes read - 1228 wordsCreating a resilient security program that meets industry standards is crucial for today’s organizations, especially with the rising expectations around data security and regulatory compliance.
For CISOs, Security Managers, GRC Specialists, and technology professionals, aligning with established frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and SOC 2 controls provides a solid foundation for protecting sensitive data and ensuring trust with clients and stakeholders.
This blog will outline how to build a security program that effectively aligns with both NIST and SOC 2, leveraging the strengths of each.
What is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a comprehensive set of guidelines developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) that assists organizations in managing and reducing cybersecurity risk. Its core structure is organized into five functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—which together provide a holistic approach to cybersecurity risk management.
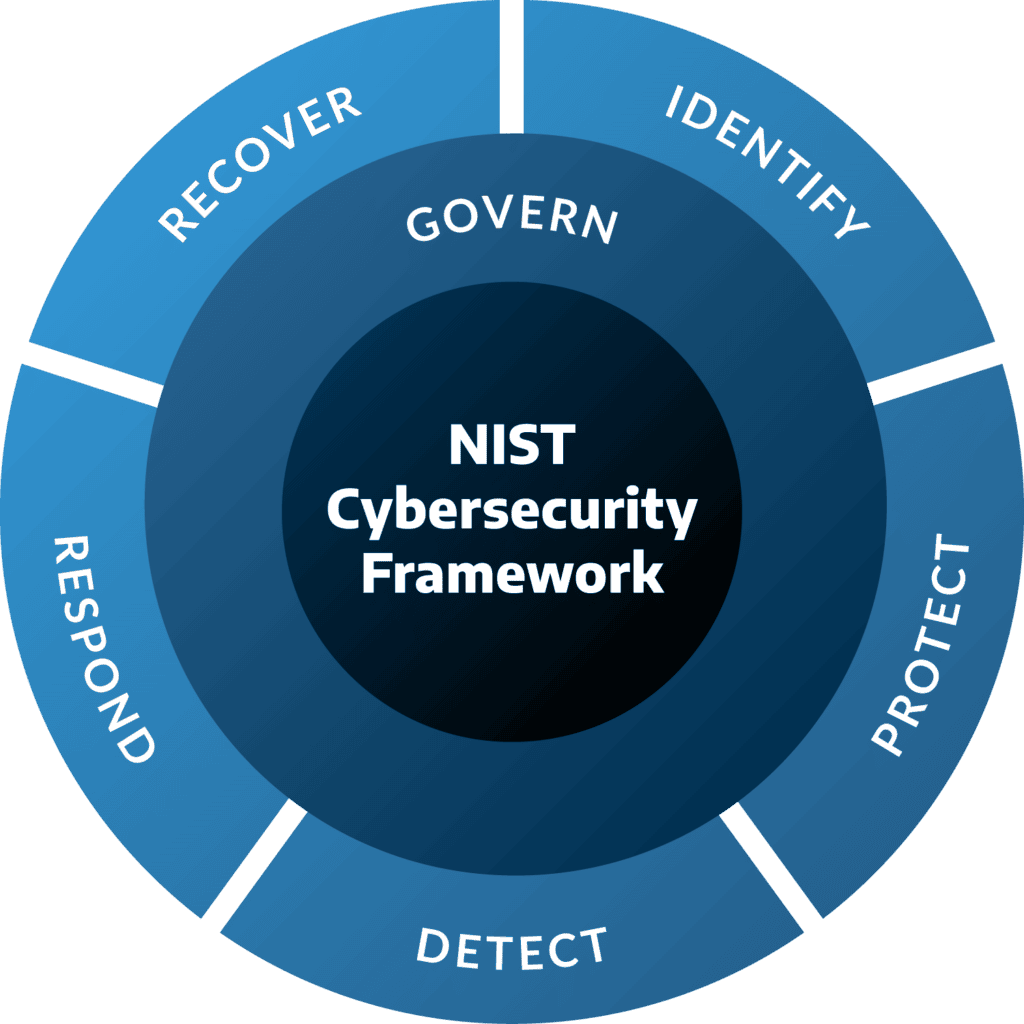
- Identify involves understanding the context, systems, and risks that define the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
- Protect covers safeguards to ensure critical infrastructure services are secure.
- Detect focuses on identifying cybersecurity events in a timely manner.
- Respond addresses response planning and mitigation for cybersecurity events.
- Recover ensures resilience and quick recovery following a cybersecurity incident.
By adopting the NIST CSF, organizations can establish a flexible, adaptive framework that scales with their needs, while also aligning with other standards like SOC 2.
Understanding SOC 2 Controls
SOC 2 is a widely recognized auditing standard developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA). It is particularly valuable for service providers managing client data as it emphasizes data security, confidentiality, availability, processing integrity, and privacy—known as the Trust Service Criteria (TSC). SOC 2 controls provide a structured approach for assessing how an organization protects information.
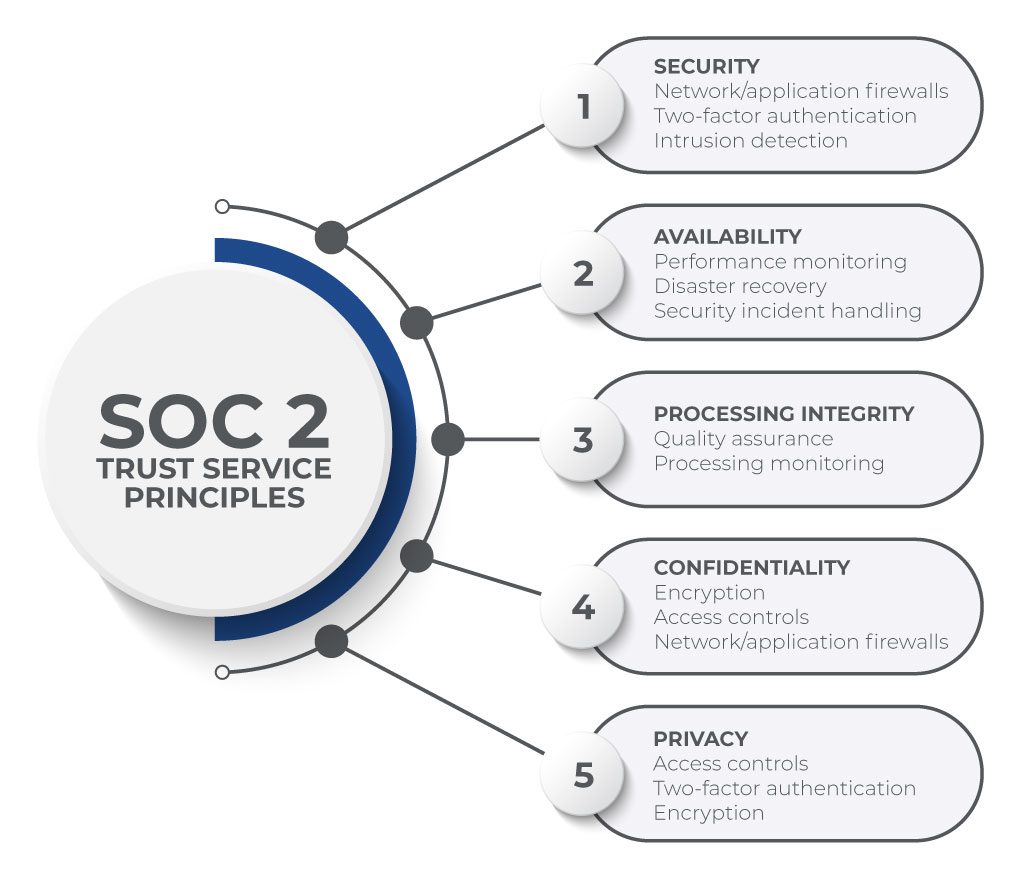
Source: CompliancePoint - SOC 2
For SOC 2 compliance, organizations must implement robust controls to safeguard information and demonstrate continuous compliance through audits. These criteria align closely with security functions in the NIST CSF, making it easier to combine both frameworks in a unified program.
Mapping NIST CSF with SOC 2 Controls
The NIST CSF and SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria overlap in many areas, making them complementary frameworks. For instance:
- Identify and Protect functions in NIST relate closely to SOC 2’s Security and Confidentiality criteria.
- Detect and Respond align well with Processing Integrity and Availability, as they ensure data integrity and service uptime.
- Recover in NIST supports SOC 2’s Availability, helping organizations maintain resilience.
Mapping these frameworks allows organizations to streamline control implementation, focusing on both risk reduction and compliance. By cross-mapping NIST functions and SOC 2 controls, companies can develop a layered security posture that satisfies both regulatory requirements and practical cybersecurity needs.
Source: ArcticWolf - Understanding and Implementing the NIST CSF
Building Blocks of a Security Program Aligned with NIST and SOC 2
To effectively combine NIST CSF and SOC 2, a security program must incorporate several essential building blocks:
Governance and Risk Management
Establishing governance frameworks is foundational. CISOs and security leaders should set policies that define the organization’s security posture, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives. Regular risk assessments help in identifying and mitigating potential threats aligned with both NIST’s Identify function and SOC 2 Security requirements.
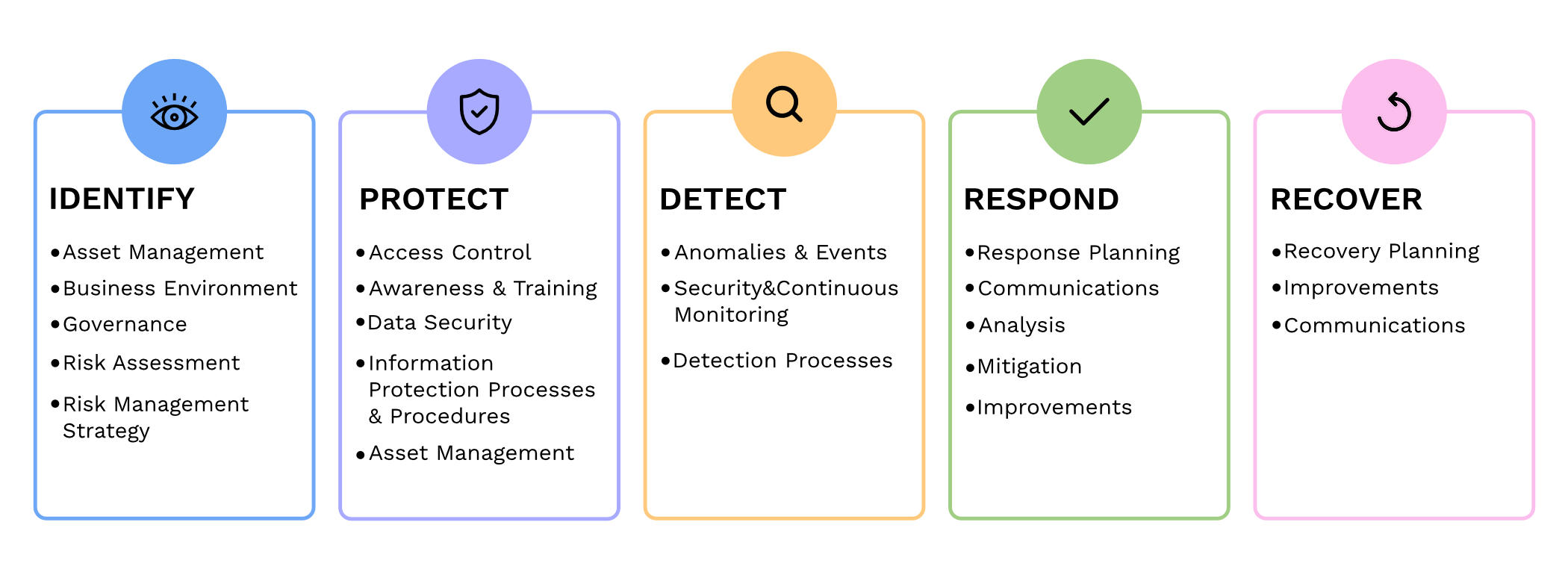
Asset Management and Inventory (Identify)
An accurate, comprehensive asset inventory is essential for identifying critical information systems, devices, and data flows. Both NIST and SOC 2 emphasize asset management to improve visibility into what needs to be protected, providing a clear basis for access control and incident response processes.
Access Controls (Protect)
Access controls are fundamental in both NIST and SOC 2 frameworks. Implement role-based access and least privilege principles to ensure only authorized individuals can access sensitive systems and data. Technologies such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthen access security and are critical in reducing unauthorized access risks.
Security Awareness and Training (Protect)
Human error remains a significant factor in security incidents, so training and awareness are critical. NIST emphasizes Protect measures, which SOC 2 reinforces through policies that require regular training on security practices, phishing, and social engineering. Continuous education empowers employees to recognize and respond to potential security threats.
Vulnerability Management (Detect)
Vulnerability management is a proactive element of both the NIST Detect function and SOC 2’s Processing Integrity criterion. Regular scanning, assessment, and prioritization of vulnerabilities should be part of the security program. Implement patch management and continuous monitoring to identify vulnerabilities before they lead to incidents.
Incident Response (Respond)
Both frameworks emphasize having a clear, structured approach to incident response. Define the process for detecting, responding to, and containing cybersecurity events. For SOC 2, logging incidents and documenting response efforts are essential for audit preparation. This step also aligns with NIST’s Respond function, helping organizations respond quickly and minimize potential damage.
Recovery Planning (Recover)
Recovery is crucial for business continuity, especially following a disruptive security incident. Recovery planning aligns with both NIST and SOC 2’s Availability criterion. Regularly test disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity plans to ensure they meet organizational requirements and function as intended during an incident.
📋 NIST & SOC 2 Security Program Checklist
Looking to align your security program with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and SOC 2 controls?
Our NIST & SOC 2 Security Program Checklist provides an easy-to-follow, step-by-step guide for building a robust security posture that meets regulatory compliance requirements. Ideal for CISOs, Security Managers, GRC Specialists, and Technology Professionals, this checklist helps streamline your security programs while ensuring alignment with industry standards.
🔍 What You’ll Get
- Comprehensive checklist with actionable steps
- Guidance on aligning with NIST CSF’s five core functions
- SOC 2 control mapping for easy compliance
- Practical tips for implementing strong security governance

Image Source: CyberSHIELD | CybersecurityOS. Gumroad
Ready to strengthen your security program? Get your checklist today!
Measuring and Improving Security Posture
Continuous improvement is a core principle in both NIST and SOC 2. Security professionals should engage in regular audits, tests, and assessments to ensure that implemented controls are effective and evolve with emerging threats. SOC 2 audits, in particular, provide a structured way to validate security measures.
Organizations should leverage metrics and KPIs that measure the effectiveness of controls across the NIST CSF and SOC 2 criteria, such as response time to incidents, vulnerability remediation timeframes, and user access compliance rates. A proactive approach to measuring and improving security posture helps maintain compliance and mitigates risks efficiently.
Conclusion
Aligning a security program with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and SOC 2 controls builds a resilient and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. For CISOs, GRC specialists, and technology leaders, this alignment enables the organization to address regulatory requirements, maintain robust security practices, and gain customer trust. A security program built on these frameworks not only helps to manage risk but also strengthens the organization’s reputation in a landscape where data protection is paramount.
Additional Resources and Recommendations
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) Overview
- SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria Overview
- Guide to Implementing NIST and SOC 2 Controls
By leveraging these resources, security teams can gain a deeper understanding of NIST and SOC 2 frameworks and apply best practices for building and optimizing a security program that ensures compliance and security excellence.
Thanks for reading,
Michael
If you enjoy the content, then consider buying me a coffee.
P.S. Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity trends and best practices by subscribing to our newsletter or leaving your thoughts in the comments below! Visit CyberSHIELD